Ad-hoc reporting is a fast, flexible way for manufacturers to create customized reports on demand, without waiting for IT support. Unlike standard reports, these are tailored to answer specific, time-sensitive questions using real-time data. This makes them ideal for troubleshooting production issues, monitoring supply chains, and tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) like efficiency and quality.
Key Takeaways:
- What It Is: A self-service reporting tool for generating real-time, customized insights.
- Why It’s Useful: Helps manufacturers respond quickly to disruptions like equipment breakdowns or supplier delays.
- How It’s Different: More flexible and immediate than standard, pre-scheduled reports.
- Setup Needs: Requires centralized data, real-time updates, and user-friendly tools within an ERP system.
- Common Uses: Inventory tracking, production efficiency, quality control, supplier analysis, and cost breakdowns.
Ad-hoc reporting empowers manufacturing teams to make quicker, data-driven decisions. When paired with a robust ERP platform like Procuzy, it integrates seamlessly with production, inventory, and supply chain data, ensuring insights are always up-to-date and actionable.
Setting Up Ad-Hoc Reporting in Manufacturing ERP Systems
Getting ad-hoc reporting up and running in your manufacturing ERP system requires careful planning. You’ll need to establish a solid technical foundation, follow a step-by-step implementation process, and set up user access controls that balance flexibility with security. Let’s break down the key requirements, setup steps, and user role guidelines to help you implement ad-hoc reporting effectively.
Requirements for Ad-Hoc Reporting
Before diving in, make sure your ERP system meets a few essential criteria for ad-hoc reporting. Start by centralizing all manufacturing data. This means consolidating information like inventory levels, production schedules, quality metrics, and supplier performance into a unified data warehouse. Without this, creating reports that cover multiple operational areas becomes a headache.
Next, your system needs to integrate data from multiple sources seamlessly. Manufacturing operations generate data from everywhere – shop floor sensors, inventory systems, quality control tools, and procurement platforms. For example, if a production manager wants to analyze machine downtime, they should be able to link it to maintenance schedules, parts availability, and production goals, all in one report.
Real-time data processing is another must-have. Manufacturing environments change fast, and yesterday’s data might already be outdated. Your ERP system should continuously update data so reports reflect current conditions. This is especially important for troubleshooting production delays or supply chain issues.
Security is also critical. Manufacturing data often includes sensitive details like production costs and supplier contracts. Your system should have role-based access controls, ensuring users only see data relevant to their roles while maintaining audit trails for compliance.
Finally, make sure your ERP system provides user-friendly report-building tools. If the interface is too complex, adoption across your organization will be slow. These tools should integrate smoothly with platforms like Procuzy’s ERP, keeping everything aligned with your manufacturing insights.
Once these foundational elements are in place, you’re ready to set up your reporting environment.
Setup Process Steps
- Map and validate your data: Start by documenting how data sources – like manufacturing execution systems, warehouse management tools, and accounting modules – connect to your ERP. Ensure data flows correctly and updates in real time.
- Configure the reporting environment: Set up the report builder interface, connect your data sources, and establish the database structures needed for ad-hoc queries. Depending on your ERP system, you may need to activate specific modules or purchase additional licenses for advanced features.
- Create starter report templates: While ad-hoc reporting is all about flexibility, providing pre-built templates can speed up adoption and ensure consistency. Templates for production efficiency, inventory turnover, supplier performance, and quality control are great starting points.
- Test and refine: Before rolling out the system company-wide, test it with power users from different departments. For example, let production managers test manufacturing reports, procurement teams validate supplier analysis, and quality control staff check inspection data accuracy. Use their feedback to fine-tune the system.
- Establish data governance protocols: Define standards for naming reports, organizing data, and sharing information. Clear documentation and accessible guidelines will help maintain consistency across the organization.
Once the infrastructure is ready, the next step is to configure user roles and permissions.
Setting User Roles and Permissions
Managing user roles effectively is all about balancing access with security. Start by categorizing roles based on job functions, such as production managers, quality control specialists, procurement officers, inventory coordinators, and executives. Each role will have different data needs and reporting capabilities.
- Production managers need access to shop floor data, like machine performance, production schedules, and material usage. They should be able to create reports across multiple production lines but don’t need detailed financial or supplier pricing data.
- Quality control specialists require data on defect rates, inspection results, and supplier quality metrics. Their permissions should allow them to drill into specific batches while analyzing historical trends.
- Procurement officers focus on supplier performance, purchase orders, and cost analysis but don’t need access to production or employee data.
To keep things organized, set hierarchical permissions. For instance, department managers might access all departmental data, while individual contributors only see what’s relevant to their tasks. This prevents information overload while ensuring everyone has the data they need.
Implement time-based access controls for sensitive data. For example, restrict financial data during month-end closings or adjust production data access during shift changes. These measures help maintain data accuracy during critical periods.
Finally, conduct regular permission audits. Review user access quarterly to ensure permissions match current roles and remove access for employees who’ve left or shifted roles. You can also use sandbox environments for safe experimentation, ensuring users can explore reporting tools without risking live data.
Key Features of Ad-Hoc Reporting for Manufacturers
Ad-hoc reporting tools can revolutionize how manufacturers process and analyze their data, enabling them to make informed decisions in complex operational environments. Here’s a closer look at the features that make these tools indispensable for manufacturing.
Custom Templates and Real-Time Data
One of the most powerful aspects of ad-hoc reporting is its flexibility. Manufacturing data streams in from a variety of sources – production lines, quality control systems, inventory databases, and supplier networks. A robust reporting tool allows users to filter and organize this data with ease. For example, a production manager might want to analyze machine performance based on specific criteria like shift, operator, product line, or time frame.
Drag-and-drop report builders simplify the process, letting users visually arrange data fields to create tailored reports. In manufacturing, where conditions like equipment performance, material availability, and production schedules can change rapidly, real-time updates from systems like manufacturing execution software or sensor networks are essential.
Customizable dashboards take it a step further, enabling users to design views that match their specific needs. A maintenance manager, for instance, could set up widgets to track preventive maintenance schedules and monitor equipment health, while a quality control supervisor might focus on defect rates or inspection backlogs. Mobile compatibility ensures that managers can access these insights on the go, whether on a tablet or smartphone, making it easier to stay informed on the shop floor.
These features empower manufacturers to generate the precise reports they need to keep operations running smoothly.
Common Manufacturing Reports
Manufacturers rely on a variety of reports to extract actionable insights from their data. Here are some key examples:
- Inventory Reports: These track stock levels, identify slow-moving items, and flag reorder points to prevent stockouts or overstocking.
- Production Efficiency Reports: By analyzing metrics like throughput, cycle times, and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), these reports can highlight inefficiencies. For example, they might reveal that one production line underperforms during certain shifts, prompting targeted improvements.
- Quality Control Reports: These focus on defect rates, inspection outcomes, and customer feedback, helping teams identify trends before they escalate. For instance, a report might show periodic spikes in defects for a specific component, hinting at supplier or process issues.
- Supplier Performance Reports: By evaluating delivery times, quality metrics, and cost trends, these reports provide a comprehensive view of vendor performance, aiding in contract negotiations and sourcing decisions.
- Maintenance Reports: These analyze downtime, repair costs, and adherence to preventive maintenance schedules, enabling teams to shift from reactive to proactive maintenance strategies.
- Cost Analysis Reports: By breaking down expenses like materials, labor, overhead, and equipment usage, these reports offer detailed insights into product costs, supporting pricing and profitability decisions.
Advanced Analytics for Manufacturing
Ad-hoc reporting doesn’t stop at standard metrics – it also incorporates advanced analytics to provide deeper insights. Here are some standout features:
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing historical equipment data, these tools can predict when machines are likely to need servicing, allowing maintenance teams to focus on what’s most urgent.
- Demand Forecasting: By combining past sales data, market trends, and external factors, these tools help manufacturers anticipate future demand, optimizing production schedules and inventory management.
- Root Cause Analysis: When issues like production delays or quality defects arise, these tools can sift through diverse data sources to pinpoint the underlying causes. For example, they might uncover that defect rates spike under specific environmental conditions or supplier delivery patterns.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): SPC tools monitor key process parameters in real time, alerting operators when metrics deviate from acceptable ranges. This helps maintain consistent quality across production runs.
- Supply Chain Optimization: These analytics evaluate supplier performance, transportation costs, and inventory levels, helping manufacturers strike a balance between cost, quality, and delivery while mitigating risks.
- Energy Consumption Analysis: Tracking power usage across production lines, these tools identify opportunities to reduce energy waste, supporting both cost-saving initiatives and sustainability goals.
Modern platforms like Procuzy integrate these advanced analytics directly into their ERP systems, offering manufacturers a unified experience and eliminating the need for separate analytics tools. This seamless integration ensures that all insights are readily accessible, helping manufacturers stay ahead in a competitive landscape.
Best Practices for Ad-Hoc Reporting
Ad-hoc reporting can be a game-changer for manufacturing organizations, but success depends on more than just having the right tools. To truly benefit, companies need clear processes, well-trained teams, and alignment between reporting activities and business goals. These steps ensure that the reports generated lead to actionable insights and measurable results.
Maintaining Data Accuracy
At the heart of effective ad-hoc reporting is reliable data. Without accurate information, even the most sophisticated reports are useless. Start by implementing data validation rules at the point of entry. For example, manufacturing systems should automatically flag errors like negative inventory quantities, implausible production rates, or dates that don’t make sense.
Consistency is key, so standardize data formats across all systems and departments. When formats vary, reports can become inconsistent, making it difficult to compare or analyze data effectively.
Regular audits are another essential practice. Schedule routine checks of critical metrics – such as inventory levels, production outputs, and quality measures – and compare system-generated data with physical counts or manual records. This helps identify and fix discrepancies early.
Assigning clear ownership of data is equally important. Designate team members to oversee the accuracy of specific information, such as inventory, production metrics, or supplier data. This not only speeds up problem resolution but also creates accountability. Additionally, leverage automated alerts to catch unusual data patterns. For instance, if production figures suddenly fall outside expected ranges or inventory levels fluctuate without explanation, these alerts can trigger immediate investigations. Modern tools like Procuzy are designed to flag such anomalies and notify the right personnel quickly.
Training Users and Driving Adoption
Once your data is in order, the next step is ensuring your team feels confident using ad-hoc reporting tools. Proper training is key to this. Hands-on, role-specific training sessions can help users understand how to generate the reports they need for their daily tasks. For example, production supervisors might focus on dashboards for equipment efficiency and quality, while procurement managers might dive into supplier performance analytics.
Start with the basics. Teach users how to create simple reports, like inventory summaries or production overviews, before introducing advanced features like predictive analytics or multidimensional analysis. This gradual approach helps build confidence and competence.
Identifying internal champions can also make a big difference. These early adopters, drawn from various departments, can help colleagues troubleshoot issues and explore new ways to use the system. Having a go-to person for questions makes adoption smoother.
Documentation is another powerful tool. Provide easy-to-follow guides with screenshots and examples tailored to your manufacturing processes. These quick references empower users to solve problems independently. Regular refresher sessions – whether monthly or quarterly – can introduce new features and reinforce best practices as your software evolves.
Connecting Reports to Business Goals
Training your team is only part of the equation. To maximize the value of ad-hoc reporting, every report should tie directly to your company’s strategic objectives. Reports without clear goals often turn into busy work, offering little value.
Define key performance indicators (KPIs) that support your priorities. For example, if reducing manufacturing costs is a goal, focus on tracking material waste and energy consumption. If customer satisfaction is a priority, monitor metrics like quality and on-time delivery.
Before rolling out new reporting processes, establish baseline metrics. Document current performance levels so you can measure improvements over time. For instance, knowing your baseline for overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) helps set realistic targets and track progress.
Timing is also crucial. Align reporting schedules with your decision-making cycles – use daily reports for operational tweaks and monthly or quarterly reports for strategic reviews. And don’t stop at generating insights – tie them to actionable plans. If a report highlights a quality issue or inventory imbalance, there should be a clear plan to address it.
Finally, make reporting processes a living part of your strategy. As your business priorities evolve, periodically assess which reports are delivering the most value. Adjustments based on feedback and results will ensure your reporting efforts remain aligned with your goals and continue to drive tangible outcomes.
sbb-itb-a748ddd
Ad-Hoc Reporting with Procuzy ERP
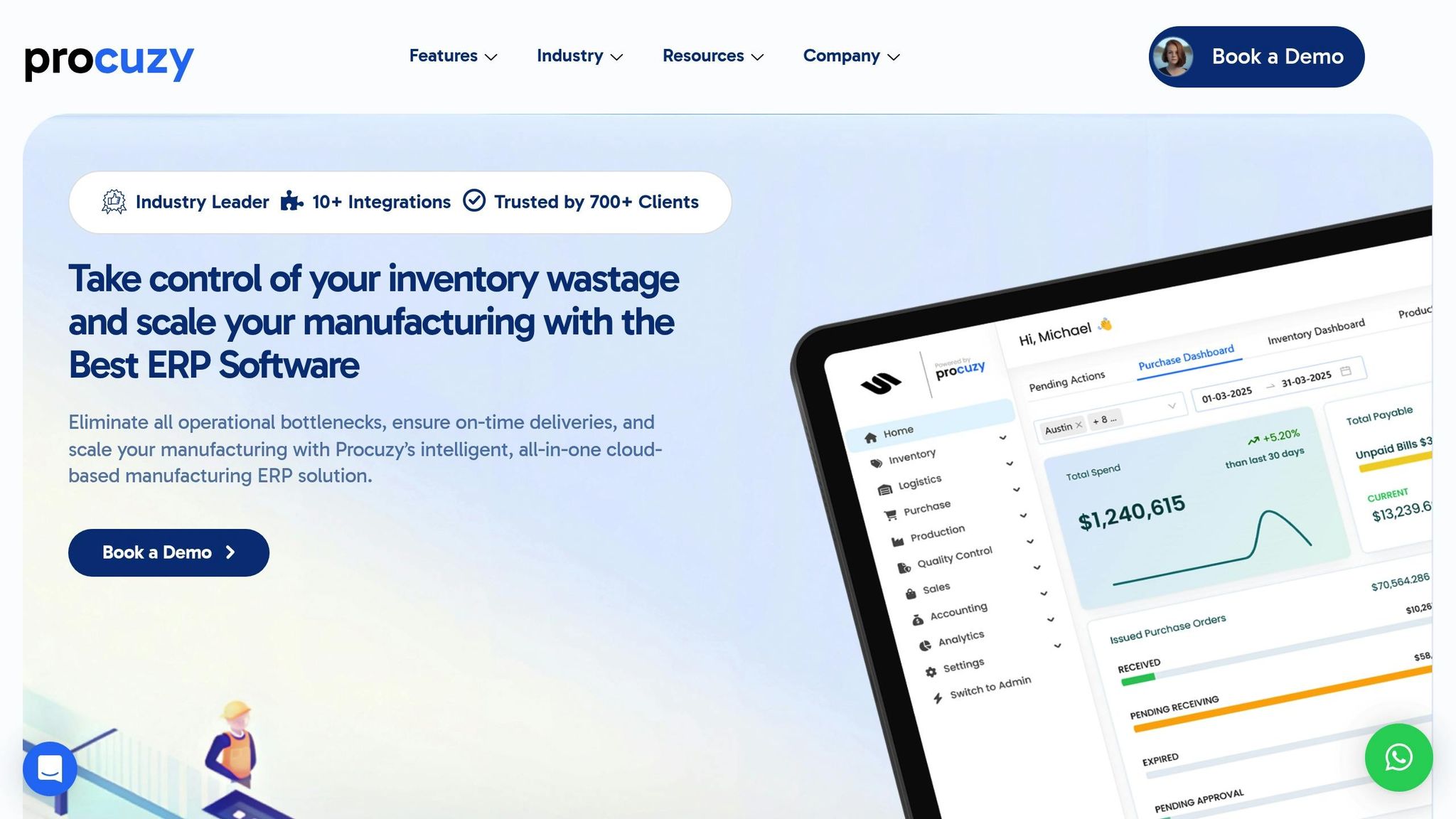
Manufacturers need flexible reporting tools that can keep up with ever-changing operational demands. Procuzy’s cloud-based ERP platform steps up with ad-hoc reporting features designed to deliver timely, critical insights. These tools are crafted to enhance efficiency and support better decision-making in manufacturing. Let’s take a closer look at how Procuzy integrates these capabilities to improve manufacturing workflows.
Procuzy’s Ad-Hoc Reporting Features
Procuzy offers Customizable Reports that allow teams to create tailored insights specific to their needs. Alongside this, its customizable dashboards provide real-time access to key performance indicators (KPIs), giving teams the data they need to act quickly. Other stand-out features include real-time inventory tracking, automated stock alerts, and batch tracking with barcoding – all working together to ensure manufacturers always have up-to-date insights.
Enhancing Manufacturing Operations with Procuzy
Procuzy’s reporting tools don’t just stop at data collection – they actively contribute to streamlining operations. By integrating production and inventory data, as well as supporting multi-location operations, Procuzy enhances demand forecasting and creates a consolidated view of manufacturing activities. Functions like production planning, quality control, and material requirement planning are all embedded within the reporting framework. This integration allows manufacturers to make informed, data-driven decisions that directly improve operational efficiency.
Unified Data Analysis and Seamless Integration
One of Procuzy’s biggest strengths is its ability to unify data from various parts of the manufacturing process into a single, cohesive reporting system. It automatically pulls data from multiple sources and updates business intelligence dashboards in real time, ensuring a complete operational overview. The platform also integrates with the Manufacturing Execution System (MES), capturing shop floor data as it happens. Additionally, it incorporates predictive maintenance and purchase order processing, giving manufacturers a consolidated view of critical metrics. By eliminating data silos, Procuzy fosters proactive decision-making and ensures that manufacturers stay ahead of operational challenges. This unified approach is a cornerstone of effective manufacturing management.
Conclusion
Effective ad-hoc reporting is a game-changer for agile manufacturing management. Unlike standard reports that follow a fixed schedule, ad-hoc reporting provides real-time, tailored insights that allow manufacturers to make quick, informed decisions. This flexibility is critical for addressing sudden shifts in demand, quality issues, or supplier delays, offering deeper, situation-specific analysis beyond routine dashboards.
For U.S. manufacturers, the advantages are clear: faster, data-driven decisions, reduced reporting costs through self-service tools, and the ability to tackle operational challenges without waiting on IT support. For example, on-demand reports can pinpoint production variances, enabling teams to adjust schedules swiftly. Real-time project monitoring, early detection of bottlenecks, and proactive machine performance tracking further ensure smoother operations, fewer delays, and lower holding costs.
These benefits hinge on a few key practices. Accurate data, supported by strong governance and reliable sources, is non-negotiable. Equally important is investing in user training to build confidence in self-service capabilities. Every ad-hoc report should align with specific business goals, such as improving throughput, enhancing overall equipment efficiency (OEE), or reducing scrap. Standardized definitions across teams ensure that insights consistently support sound decision-making.
Procuzy ERP exemplifies how integrated systems can elevate ad-hoc reporting. By centralizing inventory, production, procurement, and sales data, Procuzy provides a unified platform for real-time insights. Features like automated stock alerts, demand forecasting, batch traceability, and multi-location support eliminate data silos, enabling seamless cross-functional decisions. This centralized approach is invaluable for staying competitive in today’s fast-paced manufacturing landscape.
With self-service ad-hoc reporting powered by unified, real-time ERP data, U.S. manufacturers can make quicker, more cost-effective decisions with greater confidence – boosting throughput, cutting waste, and consistently meeting customer expectations.
FAQs
How does ad-hoc reporting help manufacturing teams make better decisions compared to traditional reporting?
Ad-hoc reporting gives manufacturing teams the tools to access real-time, tailored insights whenever they need them. This means they can make quicker, more precise decisions without relying on static, pre-generated reports that may no longer reflect current conditions.
With ad-hoc reporting, teams can pinpoint bottlenecks, monitor key performance metrics, and adjust processes on the fly. This ability to adapt in real time helps streamline operations and boosts overall efficiency, ensuring teams stay ahead of challenges and fine-tune workflows for improved results.
What are the essential steps to implement ad-hoc reporting in a manufacturing ERP system?
To make ad-hoc reporting work effectively within a manufacturing ERP system, start by laying out a well-defined reporting strategy. Pinpoint the exact questions your reports need to address, and make sure your ERP system includes intuitive, customizable tools that allow users to create reports swiftly and without hassle.
It’s also important to bring together data from different modules in real-time, enabling insights that can drive meaningful decisions. Focus on prioritizing reporting requests based on their importance to the business, and set up a clear process to manage and track these requests. Offering comprehensive training to users and limiting system access to those with a legitimate business need can also boost both accuracy and efficiency.
By taking these steps, manufacturers can use ad-hoc reporting as a powerful tool to enhance decision-making and optimize daily operations.
What steps can manufacturers take to ensure accurate and secure data in ad-hoc reporting?
To maintain accurate and secure data for ad-hoc reporting, manufacturers need to focus on a few key practices. First, ensure the reliability of data sources by thoroughly verifying them and setting up processes that uphold data integrity. Incorporating regular validation checks can catch errors early, reducing the risk of flawed decisions.
When it comes to security, implementing access controls, using encryption, and performing regular data audits are critical steps to protect sensitive information from breaches or unauthorized access. Additionally, having well-defined data governance policies in place promotes consistency and trust in the reporting process. These strategies not only protect your data but also contribute to better, more informed decision-making within manufacturing operations.
