ERP project goals are the backbone of a successful implementation. Without clear objectives, even the best ERP systems can fall short. Here’s what you need to know:
- What It Is: ERP goal setting defines measurable outcomes for your system, ensuring it aligns with your business needs.
- Why It Matters: Clear goals prevent wasted resources, keep teams focused, and help track ROI.
- How to Set Goals: Use SMART criteria (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) and involve cross-functional teams.
- Common Goals in Manufacturing: Optimize inventory, improve production efficiency, and enhance quality control.
Procuzy’s ERP system supports these goals with tools like real-time tracking, demand forecasting, and production planning, making it easier to achieve measurable success.
How to Define ERP Project Goals
Defining clear goals for your ERP project begins with a deep dive into your current operations and setting measurable objectives. The best manufacturing ERP implementations are rooted in understanding existing workflows and crafting goals that tackle specific challenges while unlocking the full potential of the ERP system. Start by examining your current processes to pinpoint areas that need improvement.
Conducting a Needs Assessment
A needs assessment lays the groundwork for effective goal setting. This involves taking a close look at key areas of your manufacturing operations to uncover inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and opportunities for improvement.
For example, evaluating inventory metrics like turnover rates, carrying costs, and stockout frequency can reveal inefficiencies. Use this data to set measurable targets, such as reducing stockouts or lowering inventory carrying costs.
Production planning is another area worth scrutinizing. Look at lead times, scheduling accuracy, and resource utilization. Often, inefficiencies stem from poor coordination between production stages or a lack of visibility into machine capacity and availability.
Don’t overlook quality control and compliance processes. By tracking defect rates, rework costs, and audit outcomes, you can set goals to improve product quality and ensure regulatory compliance.
Finally, assess procurement processes by analyzing supplier performance, order accuracy, and cycle times. These insights can help you identify ways to enhance vendor management and streamline purchasing.
Involving Cross-Functional Teams
Setting ERP goals isn’t a one-department job – it requires input from every team that will interact with the system. Each department brings unique perspectives on operational pain points and potential solutions that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Involve teams across departments to gather insights on areas like scheduling, vendor reliability, compliance, costing, and technical integration. Hosting workshops or brainstorming sessions can help prioritize these insights into actionable, measurable goals.
Once you’ve gathered input, document these requirements to create a bridge between your company’s broader objectives and the technical aspects of the ERP system.
Documenting Business and System Requirements
After completing your needs assessment and gathering input from your teams, it’s time to translate these findings into detailed documentation. This step turns high-level goals into clear, actionable ERP specifications.
Start by defining business requirements with measurable targets. Then, translate these into technical specifications, such as integration points, performance benchmarks, and compliance reporting needs.
When it comes to performance, avoid vague expectations. Instead, set specific, measurable criteria that reflect your operational needs.
Lastly, outline user access and security requirements. This includes defining role-based access controls and detailing approval workflows for various processes.
This detailed documentation acts as a blueprint for configuring your ERP system and provides a benchmark to evaluate whether the implementation meets your goals.
Best Practices for Setting and Measuring ERP Goals
Once you’ve documented your requirements, the next step is to establish goals that genuinely drive results. The success or failure of an ERP implementation often hinges on how effectively an organization sets and tracks its objectives. Clear, measurable goals not only guide the implementation process but also help evaluate its success afterward. Below, we’ll explore strategies to turn your insights into actionable and measurable goals.
Using SMART Criteria
The SMART framework is a proven method for transforming vague intentions into well-defined objectives. It provides a structure that ensures your goals are clear, actionable, and measurable.
- Specific: Goals should leave no room for ambiguity. For example, instead of saying, “improve inventory,” specify a target like reducing stockouts by using automated reorder points. This clarity ensures everyone knows exactly what success looks like.
- Measurable: Include metrics to track progress. Instead of aiming to “boost production efficiency,” set a goal like “reduce production lead times from 14 days to 10 days.” Concrete data allows for better evaluation and course correction.
- Achievable: Goals need to be challenging but realistic. For instance, if your current inventory accuracy is 75%, aiming for 99% immediately might not be feasible. A more practical target might be reaching 90% accuracy within the first year.
- Relevant: Goals must align with your broader business objectives. If your focus is expanding into new markets, ERP goals should reflect that – like implementing multi-currency support or multi-location inventory tracking.
- Time-bound: Deadlines create accountability. For example, instead of saying “improve on-time delivery,” set a target like “achieve 95% on-time delivery within six months of go-live.” This helps allocate resources and track progress effectively.
Once you’ve set SMART goals, the next step is to define success metrics that measure your progress and ROI.
Defining Success Metrics
Success metrics convert your SMART goals into tangible data points, helping you assess whether your ERP implementation is delivering the expected value. These metrics should address both operational improvements and financial outcomes.
- Return on Investment (ROI): ROI is a key metric for executives and stakeholders. Calculate it by comparing the total implementation cost against projected savings or revenue increases. For example, manufacturers often see ROI through reduced labor costs, lower inventory expenses, and improved customer satisfaction that drives higher sales.
- Operational Efficiency: Track how well the ERP system enhances daily operations. Metrics like order processing times, inventory turnover rates, and production cycle times are good indicators. For instance, if your current order-to-cash cycle is 12 days, aim to reduce it to 8 days within the first year.
- Quality and Accuracy: Monitor how the ERP system reduces errors and improves data reliability. Metrics like inventory accuracy, order fulfillment rates, and production quality percentages are critical. Many companies see inventory accuracy jump from 80-85% to 95-98% with a robust ERP system.
- User Adoption: Measure how effectively your team is using the system. Track login rates, feature utilization, and the number of completed processes within the ERP system. Low adoption often points to training gaps or configuration issues.
- Customer Satisfaction: Assess how ERP improvements impact your customers. Metrics like on-time delivery rates, order accuracy, and complaint volumes provide insight into whether internal efficiency gains translate into better customer experiences.
Adding Risk Mitigation Strategies
Even the best ERP plans can face unexpected hurdles. Including risk mitigation strategies in your goal-setting process ensures you’re prepared to handle challenges while staying on track.
- Phased Rollout: Instead of implementing everything at once, deploy core modules first and gradually add more functionality. This approach allows you to secure early wins and address initial challenges before tackling more complex areas.
- Fallback Plans: Always have a backup. Keep legacy systems accessible and outline alternative workflows to maintain business continuity in case of critical issues during the transition.
- Change Management: Resistance to change can derail even the most well-executed projects. Incorporate training programs, communication plans, and feedback mechanisms. Set specific goals for training completion rates and user satisfaction to ensure system adoption.
- Data Backup and Validation: Protect against data loss by creating detailed migration plans with validation checkpoints. Aim for high data integrity – such as achieving 99.9% accuracy during migration – to minimize disruptions.
- Vendor Support Agreements: Ensure your vendor provides adequate support. Define clear expectations for response times, issue resolution, and ongoing assistance. Include vendor performance metrics in your success criteria to hold them accountable.
Regularly reviewing and adjusting these strategies ensures your ERP project stays aligned with your goals, even as circumstances evolve. Monthly progress reviews help track metrics, refine objectives, and adapt timelines based on actual outcomes. By integrating these risk measures, you can ensure your ERP system grows alongside your business needs, paving the way for long-term success.
Common ERP Goals in Manufacturing
When manufacturers set strategic goals, they aim to address the operational challenges that often slow them down. By targeting specific outcomes with ERP systems, they can streamline processes and reduce costs. These goals are usually tied to the actionable objectives identified during the planning phase before implementation.
Optimizing Inventory Management
ERP systems are a game-changer for managing inventory more effectively. They help manufacturers free up cash, avoid production delays, and reduce waste.
- Cutting stock waste is easier with better visibility and control. ERP systems can flag slow-moving items early, giving companies a chance to adjust their purchasing strategies before waste piles up. Automated alerts also keep an eye on inventory levels, triggering reorders based on actual consumption. This reduces both overstocking and stockouts.
- Better demand forecasting takes inventory planning to the next level. Unlike spreadsheets that rely solely on historical data, ERP systems pull from multiple sources – past sales, current orders, market trends, and production capacity. The result? More accurate forecasts, smarter purchasing decisions, and lower carrying costs.
- Tracking inventory across multiple locations simplifies managing stock spread out over warehouses, production sites, and distribution centers. Without centralized insight, manufacturers often overcompensate with extra safety stock at each site. ERP systems provide real-time, centralized tracking, helping businesses allocate inventory more efficiently and cut back on excess stock.
Improving Production Efficiency
When it comes to production, the goal is clear: maximize output while minimizing waste, downtime, and resource use. These improvements directly boost profitability and competitiveness.
- Optimized machine scheduling ensures manufacturers get the most out of their equipment. Poor scheduling can lead to bottlenecks and idle machinery. ERP systems analyze production needs, machine capacity, and maintenance schedules to create efficient sequences. This reduces setup times and increases equipment utilization.
- Streamlined production planning aligns all manufacturing activities. Traditional methods often operate in silos, causing resource conflicts and missed deadlines. ERP systems integrate planning by considering material availability, labor, machine capacity, and customer priorities all at once. With dynamic scheduling, production flows can adjust in real time, improving on-time deliveries and operational efficiency.
- Reducing downtime becomes more achievable with predictive maintenance and smarter resource planning. Unplanned equipment breakdowns can bring production to a halt. ERP systems monitor equipment performance and maintenance history, predicting when upkeep is needed. This proactive approach limits unexpected failures and extends the lifespan of machinery.
Improving Quality and Compliance
Quality and compliance are critical for maintaining product standards and meeting regulatory demands. ERP systems make these goals easier to achieve.
- Meeting regulatory requirements involves detailed documentation and controlled processes. Industries like pharmaceuticals, food processing, and aerospace demand strict compliance. ERP systems automate documentation, ensuring all necessary records are captured and stored correctly. This lowers compliance risks and simplifies audits.
- Automating quality control eliminates variability and human error. Manual checks can differ between operators or shifts, leading to inconsistent results. ERP systems standardize procedures and automatically record test results, measurements, and inspections. This creates reliable quality records and reduces time spent on manual tasks.
- Complete traceability and batch tracking support efficient recalls and regulatory reporting. If a quality issue arises, manufacturers need to quickly identify affected products and their distribution paths. ERP systems track materials from receipt to final shipment, enabling targeted recalls that save money and protect the brand’s reputation. Batch tracking also allows manufacturers to trace raw materials through production, pinpointing which finished goods contain specific components.
- Analyzing quality data helps prevent future problems. Instead of just documenting issues after they happen, ERP systems analyze quality data to spot patterns and root causes. This proactive approach leads to process improvements that prevent defects from occurring in the first place.
These operational goals highlight how Procuzy’s advanced ERP capabilities can help manufacturers achieve success in their processes.
sbb-itb-a748ddd
Achieving ERP Goals with Procuzy
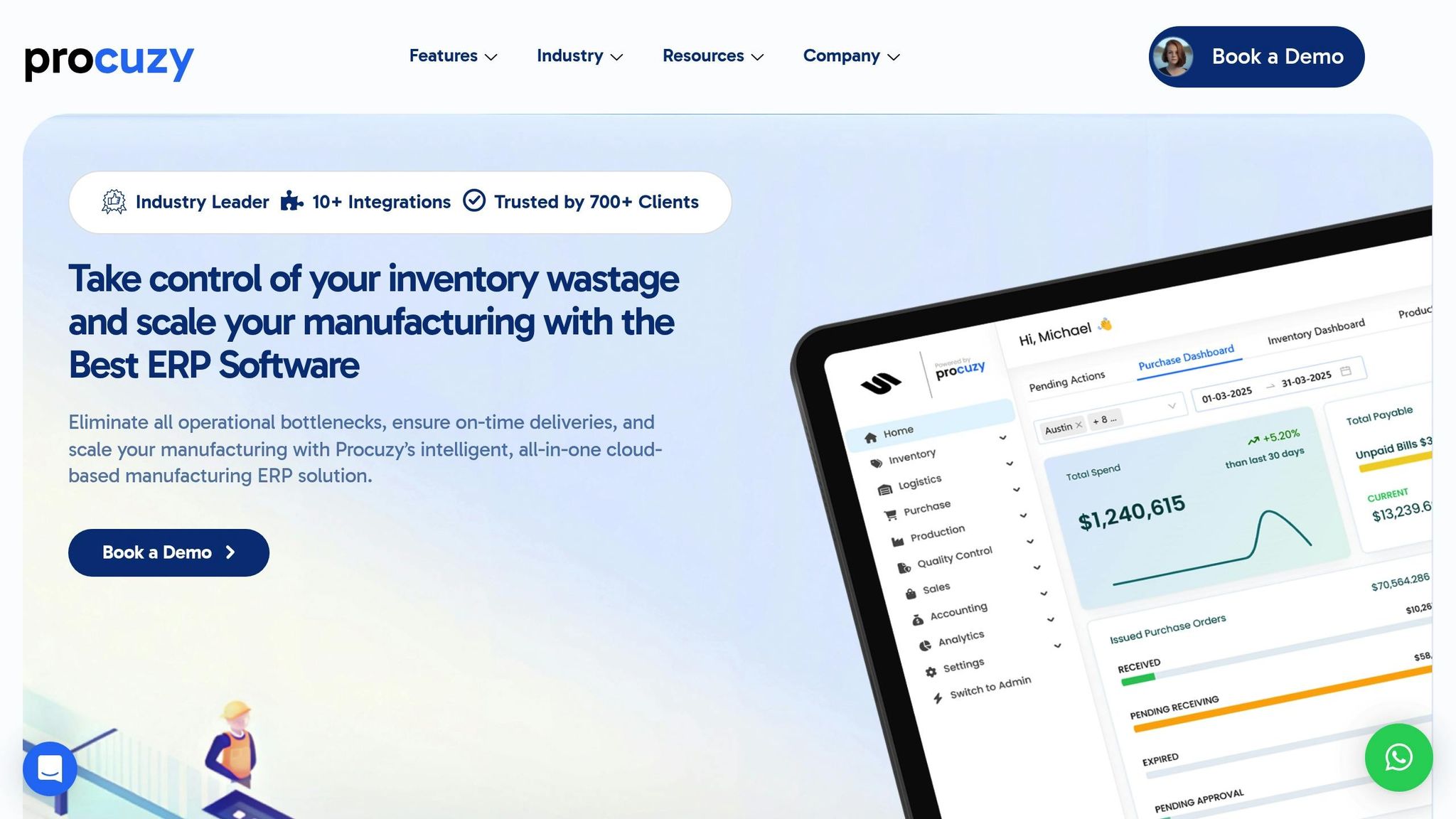
Procuzy’s platform is designed to meet the specific needs of manufacturers by addressing key challenges like inventory management, production planning, and quality control. With tools that provide real-time visibility and automate routine processes, Procuzy helps streamline operations and tackle common inefficiencies. Let’s explore how its features contribute to achieving these goals.
Procuzy’s Key Features for Goal Achievement
Real-time inventory tracking takes the guesswork out of managing stock. By offering centralized, instant visibility across all locations, it helps manufacturers avoid overstocking and stockouts. This feature ensures smarter allocation decisions and reduces the need for excessive safety stock.
Automated stock alerts complement real-time tracking by notifying teams when materials need to be reordered. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions and reduces reliance on manual monitoring.
Demand forecasting leverages historical data, market trends, and other signals to predict future product demand. With this insight, manufacturers can plan production more effectively, avoid stockouts, and ensure finished goods are available when customers need them.
Batch tracking and barcoding provide complete traceability throughout the manufacturing process. From raw materials to final shipments, every component is digitally tracked, simplifying regulatory reporting, supporting targeted recalls, and ensuring reliable documentation for certifications.
Production planning tools integrate material availability, machine capacity, and customer priorities to create unified schedules. This helps manufacturers maximize equipment usage while meeting delivery deadlines and maintaining efficiency.
Using Procuzy for Better Operations
Customizable approval automation simplifies processes like purchase order approvals, production changes, and quality checks. Workflows can be tailored to route decisions based on criteria like dollar thresholds or material types, cutting delays while maintaining proper oversight.
Material requirement planning calculates the exact materials needed for upcoming production runs. By factoring in current inventory, outstanding orders, and scheduled production, this feature reduces the risk of shortages or overstocking.
Multi-location inventory management centralizes control across multiple warehouses or facilities. This allows manufacturers to optimize inventory allocation and transfer stock between locations, lowering overall inventory costs.
Quality control features standardize inspection procedures and automatically capture test results. This ensures consistency, eliminates variability, and guarantees products meet specifications before moving on to the next production stage.
Predictive maintenance capabilities monitor equipment performance and maintenance history to prevent unplanned downtime. By identifying patterns that indicate potential issues, manufacturers can schedule maintenance strategically and avoid unexpected failures.
These operational tools work in tandem with Procuzy’s Business Intelligence Dashboards to provide a complete picture of performance.
Using Procuzy’s Business Intelligence Dashboards
Procuzy’s dashboards turn operational data into actionable insights, empowering manufacturing leaders to make informed decisions. Real-time analytics allow managers to track key performance indicators (KPIs) like inventory turnover, production efficiency, and quality metrics through continuously updated, customizable dashboards.
Stock aging insights highlight inventory that’s been sitting too long, enabling proactive decisions like adjusting pricing, running promotions, or finding alternative uses for slow-moving items.
Production performance tracking compares actual output to planned schedules across machines, shifts, and product lines. This real-time feedback helps identify bottlenecks and adjust resources to keep things running smoothly.
Financial integration ties operational improvements to financial outcomes. By connecting metrics like inventory efficiency and production quality to profitability, manufacturers can clearly see the impact of their efforts.
Customizable reporting ensures that every team has the data they need. Production managers can focus on throughput and efficiency, while executives can review financial performance and strategic indicators.
Together, these features create a unified system that addresses the interconnected challenges of manufacturing, driving improvements across the entire organization.
Conclusion and Next Steps
ERP Goal Setting Summary
To transform broad objectives into actionable outcomes, applying SMART criteria is essential. This approach ensures that goals are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. Bringing together a cross-functional team is equally critical, as it ensures that the goals address the needs of every department – whether it’s procurement, quality control, production planning, or finance. When these teams collaborate during the goal-setting phase, the ERP system is more likely to tackle real-world workflow challenges effectively.
A successful ERP implementation connects its goals to financial performance metrics. Consider objectives like reducing inventory carrying costs, improving on-time delivery rates, or cutting down production waste. Linking these metrics to system capabilities not only improves operational efficiency but also holds the organization accountable for achieving measurable results. Without clearly defined goals, an ERP system risks falling short of its potential to drive meaningful improvements.
The Role of Procuzy in ERP Success
Procuzy’s cloud-based platform is designed to address key manufacturing priorities. It simplifies inventory tracking, enhances demand forecasting, and strengthens quality control processes. Additionally, its business intelligence dashboards provide real-time insights that help manufacturers stay on track with their operational goals.
By tackling manufacturing challenges head-on, Procuzy ensures your ERP investment leads to practical improvements. Whether it’s avoiding expensive stockouts or ensuring compliance with regulations, Procuzy’s tailored features align seamlessly with the strategic objectives manufacturers aim to achieve.
Getting Started with Your ERP Project
With your goals clearly outlined and the technology ready to support them, it’s time to take actionable steps toward a successful ERP implementation. Start with a comprehensive needs assessment that includes input from all departments interacting with the system. This process will help uncover inefficiencies and pain points that slow down your operations, providing a solid foundation for setting meaningful goals.
Before implementation begins, establish success metrics to measure progress. Define baseline values for key performance indicators like inventory turnover, production efficiency, defect rates, and order fulfillment times. These benchmarks will help demonstrate the measurable impact of your ERP system over time.
Take the next step by exploring Procuzy’s scalable ERP solutions. Their team can help align the platform’s capabilities with your specific manufacturing goals, ensuring a smooth and effective implementation process. Reach out to Procuzy to get started today.
FAQs
How does involving cross-functional teams improve ERP project goal setting?
Involving cross-functional teams in setting ERP project goals promotes collaboration from the outset. It helps establish a shared vision and clear objectives that reflect the needs of all departments involved. This approach improves communication, minimizes misunderstandings, and ensures the project addresses both technical and business priorities.
With input from diverse perspectives, these teams can spot potential challenges early, propose creative solutions, and simplify decision-making. This leads to smoother workflows and makes teams more flexible when adjustments are needed during the project, boosting the chances of achieving successful outcomes.
What challenges do manufacturers commonly face during ERP implementation, and how can they overcome them?
Manufacturers face a range of obstacles when rolling out ERP systems, including steep upfront costs, integration headaches with current systems, pushback from employees, and complications with data migration. If these issues aren’t tackled head-on, they can stall progress or limit the ERP system’s overall impact.
To navigate these hurdles, businesses should focus on meticulous planning. This means conducting a deep dive into their needs and carefully reviewing existing data to make the migration process as seamless as possible. Getting employees involved early, providing thorough training, and encouraging a mindset open to change can go a long way in easing resistance. Clear communication and active participation from key stakeholders throughout the project are also critical for a smooth and successful implementation.
How does using the SMART criteria improve the success of ERP project goals?
Using the SMART criteria is a practical way to set clear and actionable goals for an ERP project. By ensuring goals are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound, businesses can create a roadmap that aligns with their priorities and allows for efficient progress tracking. This method helps keep the project focused and on schedule while making resource allocation more straightforward.
SMART goals also minimize the risk of unclear or impractical expectations. They direct attention to what truly matters, enabling businesses to measure outcomes accurately. This approach not only supports a smoother ERP implementation but also contributes to improving overall operational performance.
